Procedures
Total Hip Replacement Surgery using Direct Anterior Approach (DAA)
What is a total hip replacement (THR)?
Posterior VS Anterior Approach for Total Hip Replacement
With the posterior approach, there is a significant risk of the implants popping out (dislocating) if patients squat or cross their legs. This is because the stabilising structures at the back of the hip (capsule and muscles) are compromised during surgery. These same structures are stressed when patients squat or cross their legs.
Modern innovations in orthopaedic surgery have introduced a minimally invasive surgical technique in total hip replacement surgery. The direct anterior approach (DAA) has been widely adopted by orthopaedic surgeons across the world because of the several advantages that it yields over traditional hip replacement methods.
At Orion Orthopaedic Surgery, total hip replacement is performed using the direct anterior approach (DAA).
Dr. Mizan spent a year in Melbourne on his orthopaedic fellowship learning about the DAA technique of performing the total hip replacement. This technique preserves the muscles in the hips, by pushing muscles aside rather than cutting through them to access the hip joints.
Preservation of muscles maintains leg strength and facilitates quick recovery. By Preserving all the posterior structures of the hip, it nullifies the risk of posterior hip dislocation. After the surgery, patients are allowed to kneel, squat, and cross their legs. Another advantage of the anterior approach is that surgeons can assess the lengths of both legs accurately using X-rays since patients are lying on their back rather than on their sides.
Total hip arthroplasty via the direct anterior approach has the following benefits:
Muscles are pushed to the side during surgery (muscle preservation)
Patients lying on their backs (supine) during surgery allows for accurate assessment of leg length
Accurate X-rays are done to assess leg length and implant positioning
Hip abductor muscles are preserved
Minimal risks of hip dislocation
In a total hip replacement surgery, the worn-out bones and cartilage are carefully removed and replaced with implants. The whole procedure takes about 2 hours. With the DAA technique, patients are encouraged to walk just hours after the surgery and allowed to go home the following day. Our philosophy at Orion Orthopaedic Surgery is to allow patients to mobilize early to prevent muscle wasting and deconditioning.
What are the risks with the anterior approach?
There is a risk of transient or temporary numbness in the thigh after the surgery due to bruising of the superficial nerves in the thigh (lateral femoral cutaneous nerve). This only affects about 10% of patients and tends to resolve after several weeks.
Patients may also experience an ache in their thigh after the surgery, this is resolved with simple analgesics, physiotherapy, and time. Major complications such as injuries to large (femoral) neurovascular bundles and long bone fractures are rare.
At Orion Orthopaedic Surgery, hip replacement surgeries are performed on a simple surgical bed without any traction to prevent major complications such as spiral fractures of the femur and tibia or dislocations of the knee. A blood transfusion is also rarely needed after a hip replacement surgery.
Consultation & assessment
Appropriate imaging such as X-rays and MRI scans are required to give a better idea of the cause(s) of the pain. X-rays are important as they show the bony structures and alignment of your pelvis and hips, whereas MRI scans provide better imaging of soft tissue such as cartilage, labrum, and tendons in the hips. Both these imaging modalities complement each other and paint a clearer picture for your orthopaedic surgeon to recommend a proper course of treatment for you.
Prior to surgery, pre-operative assessments and investigations are done to ensure that the patient is medically fit for surgery. Your surgeon will also discuss the pros and cons of the procedure, including potential complications and side effects.
During hip replacement surgery
The arthritic hip joint is carefully removed with specialized orthopaedic equipment through the acetabulum (cup side) and replaced with a titanium cup. The femur stem is inserted into the femur bone before the hip is reduced into position. This surgery is performed with the use of X-rays to ensure the correct size and optimal positioning of all implants.
The orthopaedic surgeon will stress the hip in various directions during surgery to ensure it is stable and does not dislocate. After all actual implants have been positioned, the hip is washed and cleaned to help prevent any infection. The soft tissue is then closed in multiple layers before dressings are applied.
Our physiotherapist will help you on your feet several hours after surgery. This is to maintain muscle strength and restore the patient's confidence in his or her new hips. Routine medication for pain, nausea, and vomiting will be provided as required.
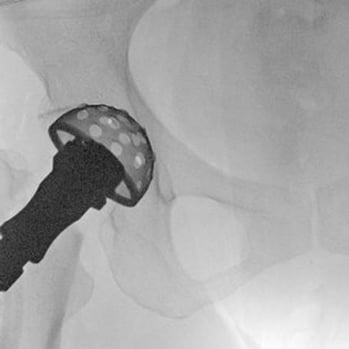 The worn-out cartilage is scraped and reamed out to make way for the new cup.
The worn-out cartilage is scraped and reamed out to make way for the new cup.
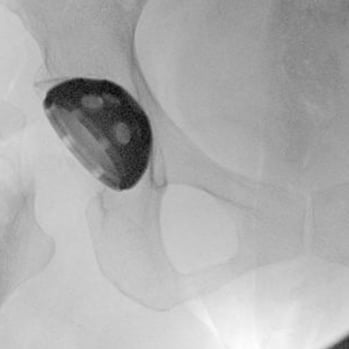 We use X-rays to ensure that the cup is appropriately sized and placed in an optimal position (medial enough with adequate inclination and anteversion).
We use X-rays to ensure that the cup is appropriately sized and placed in an optimal position (medial enough with adequate inclination and anteversion).
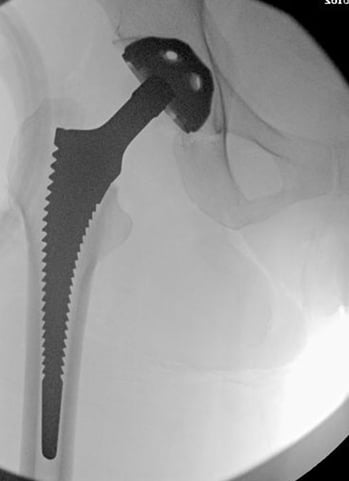 The jagged metal is a trial implant. Like buying shoes, we ensure this implant is sized appropriately and placed optimally for you.
The jagged metal is a trial implant. Like buying shoes, we ensure this implant is sized appropriately and placed optimally for you.
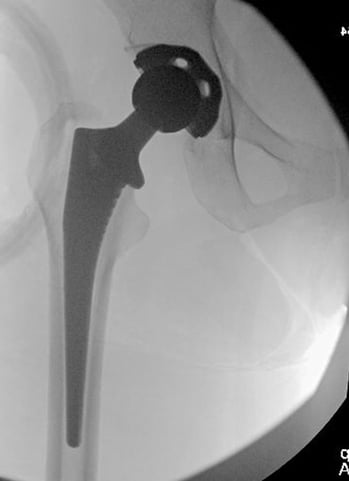 Once satisfied, we replace the trial implants with actual implants. X-rays help to ensure there are no fractures around the hip, the implants are well-sized and positioned for you.
Once satisfied, we replace the trial implants with actual implants. X-rays help to ensure there are no fractures around the hip, the implants are well-sized and positioned for you.
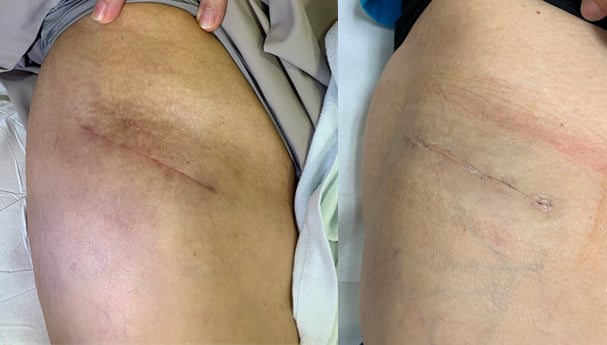
A bikini skin incision is an oblique incision about 9 to 10cm around the groin crease.
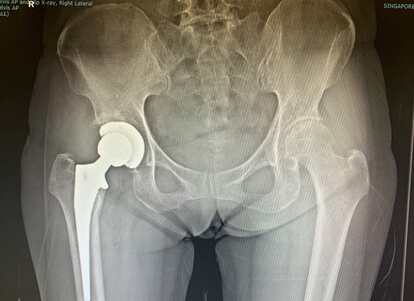
A standard post-operative X-ray is performed to assess the new hip.
Recovery Time for Hip Replacement Surgery
The time needed to recover from hip replacement surgery varies from patient to patient. Dr. Mizan’s patients who undergo the DAA Total Hip Replacement typically start walking several hours after surgery. They may walk without any walking aids or start driving at about 2-3 weeks. Most patients return to routine activities within the first 4-6 weeks. Physiotherapy and rehabilitation are important to facilitate a timely return to an active lifestyle.
Rehabilitation post-surgery
After a total hip replacement surgery via the direct anterior approach, patients are encouraged to walk as much as possible. No hip precautions are imposed and patients are allowed to kneel, squat, and cross their legs as tolerated.
Patients are informed that any activities which pull strongly on their legs are discouraged; this may include bungee jumping activities or vigorous forms of Thai Massage. The strong traction may dislocate their hips.
Most of my patients who have their right hip replaced are able to drive after 3 weeks or whenever they start to walk without using any walking aids - this is based on individual confidence in their own abilities. Patients who have their left hip replaced do not have any limitations as the left leg is not used during driving. Simple analgesics like paracetamol or anti-inflammatories are given after surgery to facilitate early mobilization.
I am always happy to hear stories from past patients returning to their favorite hobbies or sports that they were not able to do before surgery. Simple activities such as caring for their grandchildren or having lunch out with old friends are important events that raise our spirit and are important parts of our lives.
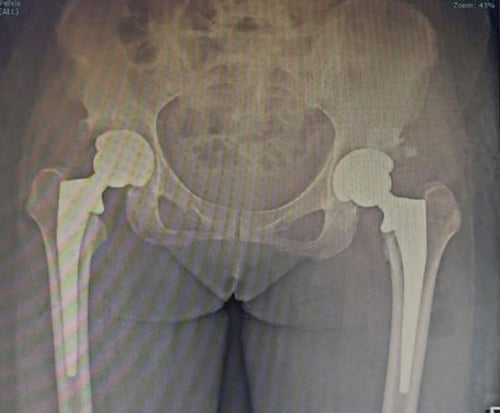
Bilateral total hip replacement performed for hip athritis secondary to dysplasia (shallow hip sockets) to facilitate a more meaningful rehabilitation in patients with several disease in both hips.
How much does hip replacement surgery cost in Singapore?
The cost of hip replacement surgery in Singapore Private Hospitals ranges from $35,000 to $45,000. This includes doctors (surgeon and anaesthetist) fees, hospitalization and facilities fees as well as implants costs. The cost is largely covered by the insurance policies which our patients have. Medisave may also be used. We provide financial counseling for our patients and facilitate the insurance claim process so they may focus on their wellbeing and recovery.
How long do hip replacement implants last?
The longevity of your implants depends on the quality and size of the implants, whether they were placed in an optimal position, your age, body weight, and the types of physical activities you indulge in.
The hip implants used in Singapore are made in the US and the manufacturing quality and storage techniques have drastically improved over the years. Several countries around the world maintain joint registries to monitor all implants that have been used and highlight major issues with defective products or implants.
A majority of patients undergo hip replacement surgery in their early 60s and above. In this phase of life, most patients are retired and do not engage in highly strenuous activities such as marathon running. The stress placed on their implants is therefore mild to moderate. Based on the average lifespan of Singaporeans which is about 85 years, we do expect most implants to be long-lasting. This is especially so if there are no infections, falls, or fractures sustained by the patient.
Younger patients below 50 years old can also experience severe wear and tear of their hip due to various reasons (developmental, infection, trauma, alcohol, medication). These patients are generally gainfully employed, and enjoy their sports and active lifestyles. The materials of hip implants in a younger patient wound include the use of ceramic bearings, which have been shown to last longer than traditional metal and plastic bearings. Younger patients are at higher risk of requiring revision surgery in the future to replace worn-out parts of their implants. In large trials, about 95% to 97% of implants are still in good working order 20 years after surgery.
Speak to our orthopaedic surgeon if you are having pain and trouble with your hips. We are here to help you on your journey.
FAQs
Can I relieve the pain without hip replacements?
Your orthopaedic surgeon will examine both your hips, knees and spine to determine if you have hip arthritis. In the early stages, conservative management with medication, physiotherapy and activity modification may be used to relieve pain from hip arthritis.
Occasionally hip injections may be administered into the hip joint occasionally to help alleviate the pain and stiffness.
If the hip pain and other symptoms persist despite conservative techniques, your orthopaedic surgeon will then discuss other minimally invasive or surgical techniques.
When do you consider hip preservation surgery?
In young patients with hip pain and arthritis, hip preservation surgery may be ideal. Depending on the underlying cause of hip pain, the orthopaedic surgeon may repair labral repairs arthroscopically, or perform core decompression surgery for early avascular necrosis (death of bone tissue) of the hip.
Where patients are older or if hip preservation surgery is not appropriate, a total hip replacement (THR) is preferred. In patients with debilitating hips and poor quality of life, we perform THR so that they may return to their active and meaningful lifestyle. We want a good quality of life now rather than see life pass us by just because of a painful hip.
Make an appointment with Dr Mizan Marican of Orion Orthopaedic Surgery today to put an end to your hip pain.
Is it alright to walk around with a sprained ankle?
This depends on the sprain's severity and what treatment has been rendered for the injury. Your doctor may advise you to only put minimal weight on your ankle while it is still recovering from the injury. Excessive walking may lead to more pain and swelling if the injury is stressed too early on.
How do I know if my ankle sprain is serious?
The nature of the initial accident or injury will provide a good idea about how fast it may recover. A serious injury is characterized by severe pain, swelling, and recurrent sprains despite efforts to support and treat it. If you are experiencing these, the soonest visit to the specialist is highly advised.
Can I claim insurance for my ankle injury?
Ankle sprains and injuries are insurance claimable. We do advise our patients to check with their personal or corporate insurance plans and representatives. We are also able to help them with this if required.
What should I do immediately after an ankle sprain while waiting for my appointment and treatment?
Timely self-care with rest, icing, compression, and elevation are important to manage the initial pain and swelling around the ankle. Anti-inflammatory medication will further reduce the pain and swelling that you may be experiencing.
I have more questions, how can I speak to a doctor?
Please call us at +65 6733 4565 (during office hours), or drop us a text or WhatsApp message at +65 9766 4565. We will reply to your queries as soon as we get them. You may also call to make an appointment to see Dr. Mizan for your ankle injury.
