Procedures
Total Knee Replacement Surgery in Singapore
Osteoarthritis: The most common reason for knee replacement surgery
What is Osteoarthritis and how does it affect the knee?
Osteoarthritis describes the degeneration of cartilage in a joint. While it can affect any joint, the symptoms are most commonly felt in the knees, hips, and spine. The knee is the largest joint in the body and is made up of the femur (thigh bone), the upper end of the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (knee cap). The cartilage that covers the ends of our femur bone and tibia bone is like coconut flesh; white, thick and ultra-smooth. Arthritis occurs when the soft cartilage in our knee wears out due to various causes like degeneration, wear and tear, malalignment of the knee, trauma and infection. This previously intact cartilage starts to break down and offers less support and protection to our knees. Apart from the degenerative type of arthritis like osteoarthritis, there are also inflammatory types of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. In this article, the term “arthritis” may refer to either or both kinds of conditions.
What are the signs that I may have arthritis in the knee?
You may have knee arthritis if you experience:
- Pain and swelling in the knee. The pain in the knee joint can be sudden or progressive.
- Difficulty walking
- Clicking, creaking, grinding, or snapping sounds when you move your knee joints
- Severe joint stiffness
- Your knee suddenly buckling or giving out
- Locked knee (your knee cannot be bent or straightened)
When does it happen and does it get worse?
Osteoarthritis often develops after the age of 50-60 years old while inflammatory arthritis occurs earlier between 30 and 50 years of age. These conditions are worsened by obesity, malalignments of the legs or trauma.
There are two menisci in each knee which act as shock absorbers. They are crescent-shaped and help distribute weight in the knee as well as lubricate and stabilize the knee. Degeneration of our cartilage and tears in our meniscus often occur together and contribute to the symptoms of knee arthritis. Arthritis creeps up on us ever so slowly; it starts with intermittent pain but usually progresses into constant pain and stiffness which affects our daily functions. This condition actually affects millions of people around the world and is a major cause of lost work time and disability.
Can knee arthritis be prevented?
We can prevent arthritis by maintaining healthy body weight and participating in moderate amounts of aerobic exercise regularly. A healthy diet and lifestyle coupled with strong muscles help keep arthritis at bay.
What about medication?
Glucosamine and chondroitin used to be regularly prescribed for the treatment or prevention of knee arthritis. The latest guidelines from the American Association of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) do not support the use of glucosamine or chondroitin for the treatment of arthritis. There are patients who feel these supplements significantly improve their symptoms. They may continue with them as long as they do not interfere with other medications or diabetic control.
Knee injections have been shown to help patients with knee arthritis. These include hyaluronic acid which lubricates the knee as well as newer injections that use patients’ own blood (autologous protein solution) to help reduce inflammatory cytokines in the knee. These cytokines or bad proteins are thought to compromise the integrity of cartilage and cause arthritis. While they are safe and have been shown to improve the symptoms of arthritis, current research is being done to determine the positive effects of these blood injections for knee arthritis.
Surgical Interventions
In the early stages of arthritis, much can be done to try and preserve the knee. Multiple surgeries have been done over the years to either replace the focal loss of cartilage or help to regenerate it. These include transplanting cartilage from other parts of the knee into the defect (OATS: osteochondral autograft transfer system) or harvesting and growing a small piece of cartilage in a lab before re-implanting it into the knee (ACI: Autologous chondrocyte implantation. A common procedure we have done for years and still continue to perform is the microfracture surgical technique. While the cartilage has no blood supply of its own and therefore cannot regenerate, the bone beneath it does. During a keyhole (arthroscopic) procedure, a long and fairly sharp instrument is used to penetrate the surface of the femur bone. This induces some bleeding from the bone itself. The blood supply coming out contains cells that have the ability to develop into cartilage (fibrocartilage) over time. This new fibrocartilage is not as robust as your native cartilage (Hyaline cartilage) but at least there is some cartilage to reduce the pressure and pain from arthritis. Where the cartilage loss is very diffuse and widespread, these knee preservation techniques do not work.
Why do patients have knee replacement surgery?
Most patients have knee replacement surgery as a last resort after experiencing pain and disability for some time. Loss of function such as the inability to walk, climb stairs and enjoy sports and hobbies persuades patients to have surgery. Some have deformities around their knees such as bow-leggedness or knock-knees which affect their gait and quality of life.
Doctors and surgeons would usually help patients with their symptoms using conservative techniques such as medication, rehabilitation/physiotherapy and injections. Knee preservation techniques such as meniscus and cartilage repairs may also be employed. If these techniques fail or if the condition of patients’ knees is too severe, a replacement procedure may be considered.
What types of knee replacement surgeries are there?
There are two main types of knee replacement surgeries:
- Partial knee replacement
- Total knee replacement
- Others
Partial Knee Replacement Surgery
There are three main compartments in the knee; the medial, lateral and patella-femoral compartments (front) of the knee.
Partial or Unicompartmental knee replacement surgery only replace one compartment which are affected by arthritis, leaving the other healthy compartments alone. The medial or inner compartment of the knee is most commonly replaced. The benefit of this surgery is to preserve as much of the knee as possible, allowing patients to enjoy a more ‘normal’ feeling of the knee. The surgical scar is smaller and recovery much faster than a total knee replacement.
These operations are often done for patients who are still very active with their sports and hobbies and whose knees are not bad enough to require a total knee replacement. For partial knee replacements to be successful, patients must have good flexion of a stable knee, an intact Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and cannot have inflammatory arthritis (eg. rheumatoid arthritis, gout), amongst other factors.
Total Knee Replacement Surgery
A total knee replacement (TKR) describes a procedure to remove the worn-out parts of the knee and replace them with implants. Healthy bones and ligaments are left behind to accommodate the metal femur and tibia implants and the plaster liner between the two metal pieces. Your orthopaedic surgeon may also replace your patella if there is significant wear and if your patella bone is large enough. A TKR is done to restore motion and function to the knee, enabling our patients to return to an active lifestyle.
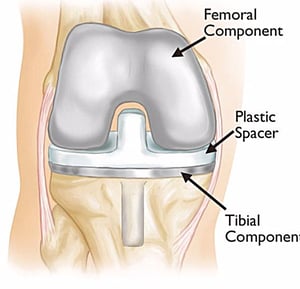
If your knee pain is mostly around your kneecaps (patella), Dr. Mizan will determine if you are suited for patellofemoral joint replacement surgery, also known as knee cap replacement surgery. This may be done as part of a total knee replacement procedure. X-rays and MRI scans will be done to assess the cartilage damage in your knee before deciding which procedure is best suited for you. If the cartilage in other compartments of the knee is affected, a total knee replacement including resurfacing the patella might be more appropriate for you.
Knee Cap Replacement
Other types of knee replacement surgery
Two or Bicompartmental knee replacement surgery is seldom performed compared to uni (one) compartment or total knee replacement surgery. This is because if two compartments already need to be replaced, it won’t take long before the third compartment of the knee also wears out and start to cause pain. Two different implants are also harder to insert in an optimal way compared to a total knee replacement prosthesis. If two compartments are already worn out, Dr Mizan prefers to perform the total knee replacement procedure as it has better long term survivability and long-term data throughout the world. A single long lasting procedure if preferable rather than two big operations just a few years apart.
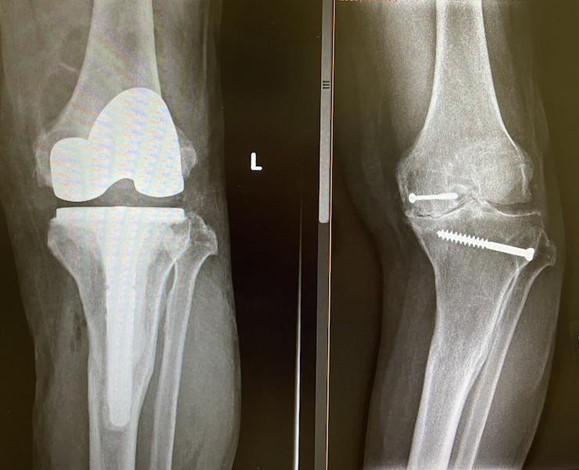
Revision knee replacement surgery refers to a repeat operation from a previous surgery. This may happen months or years after the first index operation and due to a variety of reasons. Some patients undergo revision knee surgery due to persistent pain, stiffness, loosening or infection.
Robotic-assistant knee replacement
Robotic-assisted technologies have been a revolutionary tool for joint replacement surgery around the globe. It removes the guesswork and inconsistencies out of a complex operation and patients benefit from well-placed implants with great knee function after surgery.
There are several robotic systems on the market at the moment (Zimmer Rosa, Mako Stryker). These systems use pre-operative imaging such as X-rays or CT scans of patients legs and knees to get a detailed two or three-dimensional assessment of the knee joint itself. This allows planning to be done before surgery to determine the size of the implants as well as accurate surgical plans to place these implants in an ideal position for each patient.
During the surgery itself, Dr. Mizan makes further assessments of the knee with navigational techniques to ensure that the surgical plans are accurate. Even before a single bone cut is made, we can trial different-sized implants in different knee positions and make micro-adjustments along the way. The numbers on the screen reflect how well your knee moves during extension and flexion, as well as its stability during stressed conditions. We only proceed to make the first bone cut and position the implants in your knee after we are satisfied with the data provided by computer software.
The robotic arm has been programmed to allow the surgeon to only cut the bone according to the surgical plan. If the bone cut deviates from the plan, the robot will freeze and the orthopaedic surgeon will have to withdraw and start again with the planned bone cut. This ensures the precision of the bone cuts and implant positioning and prevents collateral injury to the adjacent soft tissues. Patient safety is our number one priority!
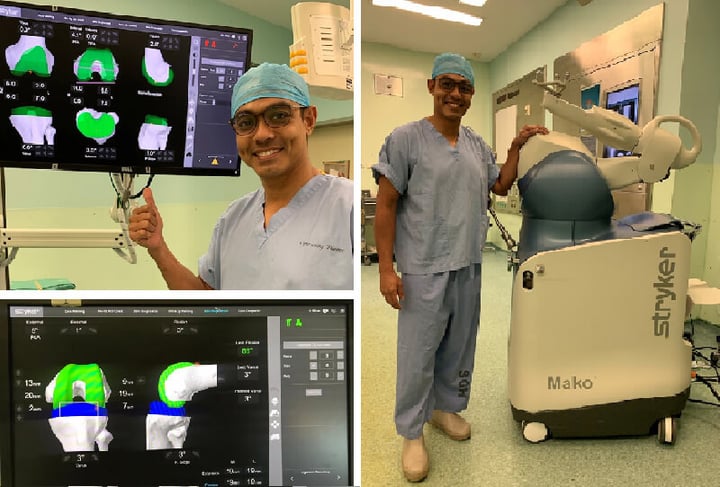
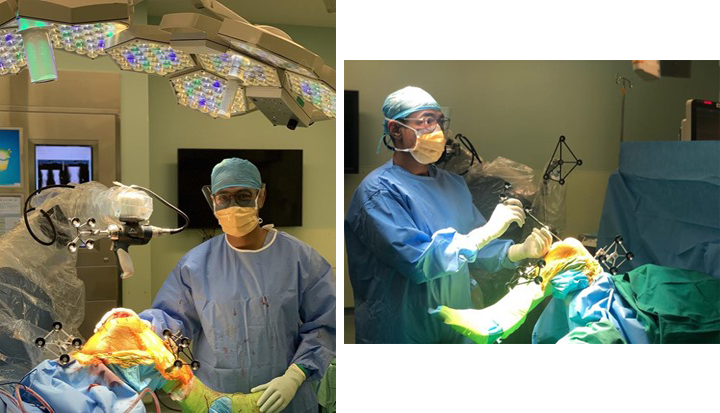
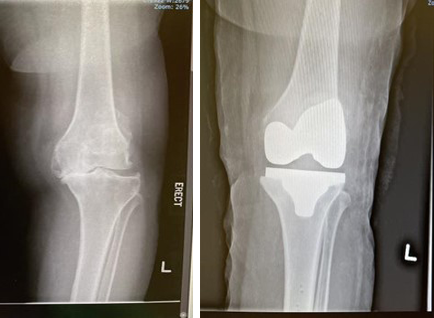
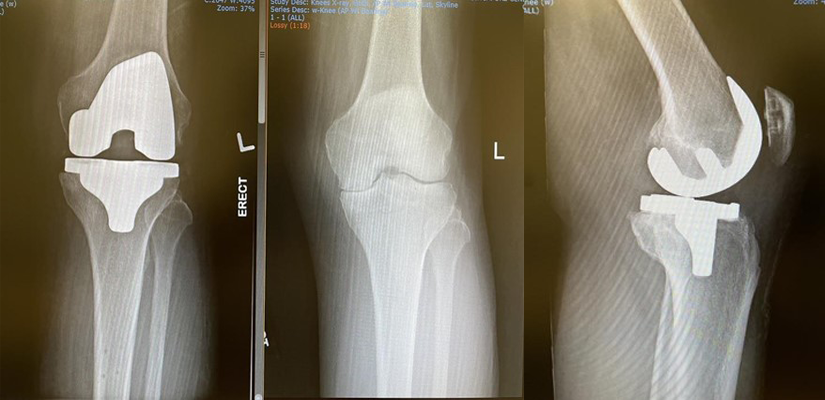
What to expect if I’m having a Mako robotic knee replacement?
Once a decision has been made to perform the MAKO robot-assisted knee replacement, Dr. Mizan will organize the CT scan of your knee as part of the pre-operative preparations. The surgery itself will take about 90 minutes or so. During surgery, most patients receive either a spinal anaesthetic or a general anaesthetic. You will be able to start walking the day after surgery with the help of a walking frame and physiotherapist.
Most patients stay in hospital for about 3 to 5 days, this depends on how well they walk and climb stairs. Patients are discharged with some oral medication and must continue their physiotherapy in the outpatient setting. Dr. Mizan will follow you up every week for about 3 weeks then this may be changed to once every few months.
Sports and hobbies after surgery
Most patients can return to low-impact sports after knee replacement surgery. This differs from patient to patient and also depends on the type of sports involved. We recommend low-impact aerobic exercises to strengthen muscles and regain the mobility of your knees. These include walking, gentle jogging, cycling and swimming. While some patients return to sports and hobbies early, some are known to take almost a year before their knee feels ‘normal’.
Knee replacement surgery is aimed at improving your function and quality of life for as long as possible. Activities that may shorten its lifespan by causing excessive wear/erosion and loosening include having excessive body weight, high-impact sports and trauma.
Physiotherapy plays a crucial part of your rehabilitation after knee replacement surgery. It is performed in several phases focused on management of knee swelling, return to normal walking patterns, muscle strengthening, balance and flexibility. Our Physios also teach patients certain rehab techniques which they may do themselves in the comfort of their own home so that their benefits are long lasting.
What is the recovery like after surgery?
Most patients stay in the hospital for about 3 to 4 days for pain medication and physiotherapy before returning home. We encourage patients to stand and walk as soon as they can to maintain their muscle strength and confidence. Physiotherapists will be present during the hospital stay as well as after discharge to assist with the rehabilitation.
We provide walking frames and crutches for patients during the first few weeks after surgery. These walking aids help patients on their road to recovery while they are still a little unsteady on their feet.
Dr Mizan will follow patients up in the clinic every 5 to 7 days after surgery to ensure that the surgical wound heals well and that patients are progressing with their rehabilitation. After the first few weeks, follow-up appoints are about 2 to 4 months apart to allow patients to have meaningful physiotherapy and rehabilitation. Knee swelling can be managed with medication and ice along the way.
Cost of knee replacement surgery in Singapore
Knee surgery in Singapore private hospitals cost between $40,000 and $45,000, depending on the type of surgery, implant, as well as inpatient and outpatient charges. This amount includes hospitalization and use of the operating theatre, cost of implants and medications as well as doctors’ (surgeon and anaesthetist) professional fees. At Orion Orthopaedic Surgery, we provide financial counseling to our patients and guide them on insurance matters so they may focus on their rehabilitation and recovery.
Is Post-Surgery Scarring Normal?
There will be a 10 to 15cm scar in the front of your knee after the surgery. This surgical incision is needed to adequately expose the knee to remove all the worn-out parts as well as place the new implants in an optimal position. While keyhole surgery may be used in knee preservation techniques such as meniscus repairs, it cannot be used for a formal total knee replacement. Skin incisions that are too small may even compromise the surgery as the surgeon may not be able to have adequate visualization of critical areas and implants may not be placed optimally. The surgical incision takes two weeks to heal while swelling takes about a month or so to resolve. During this time, dressing changes are done to prevent infection and facilitate good healing.
How to reduce swelling
There are several techniques we employ to help reduce knee swelling. Immediately after surgery, your knee will be wrapped in wool and crepe dressing. This compression helps prevent bleeding into your knee after surgery. The day after surgery, this compression dressing is lightened and ice packs are applied to further reduce swelling. Finally, the elevation of the foot with pillows under the ankle helps reduce the swelling. Swelling around the knee may last for a month or two in some patients. This is completely normal and will improve from day to day.
Rehabilitation
Patients are encouraged to do as much walking and aerobic exercises as they wish. This helps to develop their general muscle strength and flexibility. Our patients usually report improved quality of life and physical function after their surgery. They also experience better knee extension and flexion. Squatting is something not everyone is able to achieve after a knee replacement. A lot of it depends on how much they were able to flex their knee before surgery; how large their thighs and calf muscles are and the strength in their legs to actually perform a squat and stand up after that.
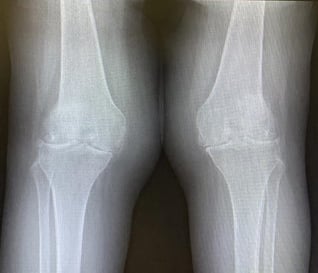
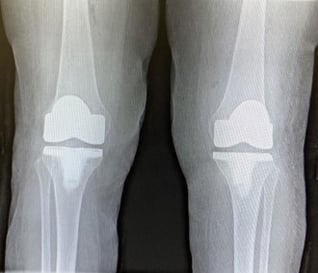
Bilateral Knee Replacement
Some patients have returned to get the same operation performed on their other leg. After they have recovered from their first knee replacement and are satisfied with the results, they then want the same surgery on the opposite leg with confidence. A bilateral knee replacement is occasionally performed in patients who have severe symptoms in both knees and are very affected by them. In this group of patients, their rehabilitation will not be optimal if a total knee replacement surgery is only performed on one knee. At Orion Orthopaedic Surgery, we ensure that they are of the appropriate age and have minimal medical conditions so that they are suitable candidates for the procedure. Depending on individual patients, patients who have had a bilateral total knee replacement are only asked to walk 2 days after surgery instead than 1. This is to ensure their pain control is taken care of, they do not have any dizziness or vertigo and they have enough confidence to start their physiotherapy.
Caption: Both knees are painfully affected by rheumatoid arthritis, an inflammatory condition that frequently affects all compartments in both knees.
Caption: A bilateral total knee replacement is done to facilitate a meaningful rehab program and return the patient to gainful employment
Do speak to us if you are having pain or stiffness around your knees. Dr. Mizan would be delighted to give you some advice for your symptoms.
Is it alright to walk around with a sprained ankle?
This depends on the sprain's severity and what treatment has been rendered for the injury. Your doctor may advise you to only put minimal weight on your ankle while it is still recovering from the injury. Excessive walking may lead to more pain and swelling if the injury is stressed too early on.
How do I know if my ankle sprain is serious?
The nature of the initial accident or injury will provide a good idea about how fast it may recover. A serious injury is characterized by severe pain, swelling, and recurrent sprains despite efforts to support and treat it. If you are experiencing these, the soonest visit to the specialist is highly advised.
Can I claim insurance for my ankle injury?
Ankle sprains and injuries are insurance claimable. We do advise our patients to check with their personal or corporate insurance plans and representatives. We are also able to help them with this if required.
What should I do immediately after an ankle sprain while waiting for my appointment and treatment?
Timely self-care with rest, icing, compression, and elevation are important to manage the initial pain and swelling around the ankle. Anti-inflammatory medication will further reduce the pain and swelling that you may be experiencing.
I have more questions, how can I speak to a doctor?
Please call us at +65 6733 4565 (during office hours), or drop us a text or WhatsApp message at +65 9766 4565. We will reply to your queries as soon as we get them. You may also call to make an appointment to see Dr. Mizan for your ankle injury.